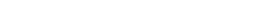6 Stages of Financial Life: Independence, Growth, Stability & others
The human being, throughout his life, goes through different stages with different needs. Let us not forget that we need to know where we want to go, being essential where we are, in order to recognize when we have arrived.
Financially speaking, it is no different, and the individual needs at each stage of his life some financial needs with certain characteristics. These needs will be covered by the different financial products adapted to each specific stage.
Acquiring an adequate financial education in order to enjoy economic autonomy is one of the most complicated processes a person faces throughout his or her life.
Finance is not a matter of a few people who devote themselves to it as a profession. We should all have some basic knowledge to avoid deception, as well as address the doubts that arise at any stage of financial life.
The financial markets will always be fluctuating. And our financial needs are also subject to change over time. And this is inevitable. This being so, a financial strategy is necessary to assume and face all the needs, both financial and personal, that arises.
Depending on age, a person’s financial life can be divided into the following six stages, each with a set of specific characteristics.
6 Stages of Financial Life
First Stage (0-18 years) – Formation: It is the period of learning and training par excellence, marking the future financial decisions and shaping the financial behavior. Educators must emphasize the value of money and the need for savings. Expenses are not a concern as they are typically taken care by parents or guardians.
Second Stage (19-30 years) – Independence: The financial future begins. Starting with financial independence when an individual earns his first income. And the need to invest in the financial products arises. The creation of a patrimony of both assets and liabilities begins. The savings horizon is short term without excessive reserves for unforeseen events. Generally speaking, the first good acquired (liability) is a vehicle.
Third Stage (31-45 years) – Professional Growth: Both income and expenses increase. Investments are focused on increasing family wealth. The expenses are generated from within the family itself caused by the acquisition of essential goods. It is the stage where the most important investment decisions are planned.
Fourth Stage (46-55 years) – Professional Consolidation: The income is consolidated and the basic family patrimony is finished. And there begins the focus in the saving for the retirement. Savings has a future projection and financial products are more complex than in previous stages. The goods that were acquired in earlier stage are destined to increase in the patrimony of assets.
Read more: Best jobs after retirement for Indians.
Fifth Stage (56-65 years) – Stabilization: Income stabilizes and family expenses fall. With basic needs covered, more capricious products are consumed. Family wealth tends to increase. It is the stage where one prepares, by proximity, the retirement to enjoy the golden stage.
Sixth Stage (more than 65 years) – End of Active Life: The active life is considered over and income decreases. Consumption will depend on the savings of the past stages and is based on enjoyment. Investments become more conservative, trying to guarantee liquidity. The development of this stage will depend very much on the financial planning carried out in the past. The mistakes that were made earlier will hardly have any specific solutions in this period. Financial needs are satisfied by the amount we have accumulated over the other five stages. In this stage, the results of the examinations that the financial life has put us through the previous stages are shown, with no option for recovery in the event.
Check out: Best part-time jobs for seniors after retirement in USA
Therefore everyone’s financial life must respond to these basic concepts: development of financial habits, accumulation of wealth, conservation and enjoyment of it.